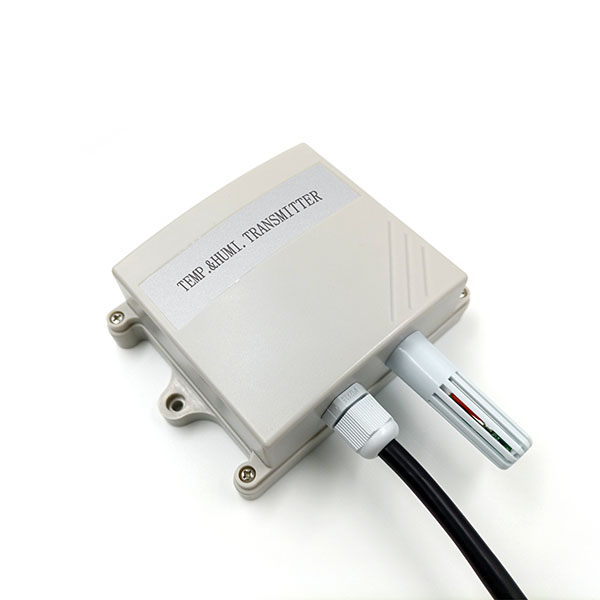
How industrial temperature sensors work
Temperature, one of the seven fundamental quantities of the International System of Units, is a parameter that needs to be monitored in industrial sites.
In industrial production, temperature sensors are commonly used to monitor the temperature of machines and equipment to ensure that they are operating within their normal operating range. So, what are the Industrial temperature sensors? Let’s give you a quick overview today.
Types of Industrial temperature sensor
A industrial temperature sensors is a sensor that senses temperature and converts it into a usable output signal. Temperature sensor is the core part of the temperature measurement instrumentation, a wide variety of varieties, according to the measurement method can be divided into two categories of contact and non-contact, the temperature sensor commonly used in the industry at present, there are four categories, respectively, thermocouples, RTD resistance RTDs, thermistors and integrated circuit temperature sensors.
Thermocouple - wide measurement range, cost-effective
Thermocouple is to connect one end of two different materials of metal (metal A and metal B), when the thermocouple end is heated, there is a potential difference in the thermocouple circuit. The measured potential difference can be used to calculate the temperature.
It is the most commonly used temperature sensor for temperature measurement. Its main benefits are a wide temperature range and adaptability to a variety of atmospheric conditions, as well as being robust, inexpensive, and requiring no power supply, and the cheapest.
Thermocouple type temperature sensors are widely used for temperature measurement in industrial sites because of their large range, low cost, fast response and good durability. However, they also suffer from small output voltages, susceptibility to noise from wire loops, and high drift.
In short, thermocouples are the simplest and most versatile temperature sensors, but they are not suitable for high-precision measurements and applications.
RTDs - the most stable and accurate
RTDs are usually made of platinum, so RTDs are also called platinum resistors, and some are made of nickel or copper. resistance varies with temperature, and the temperature can be measured by measuring the change in resistance value of the sensing RTD. RTDs can be made in many different shapes, such as wire-wound, thin-film, and so on.
RTDs are the most accurate and stable temperature sensors, and their linearity is superior to that of thermocouples and thermistors.
Therefore RTDs are best suited for applications where accuracy is critical.
Thermistors - Compact Size, Fast Response
Thermistors are usually made of ceramic materials such as nickel, manganese or cobalt oxides plated in glass, which makes them susceptible to damage. The principle is that the resistance value of a metal changes as the temperature changes. For different metals, the resistance value changes differently for each degree of temperature change, and the resistance value can be used directly as an output signal.
Thermistor because of the use of semiconductor, so most of the negative temperature system, that is, the resistance value with the temperature increases and decreases, and a small change in temperature will cause a large change in resistance value, so it is the most sensitive temperature sensor.
However, thermistors have very poor linearity and exhibit highly nonlinear resistance-temperature curves. Thermistors are very small in size, respond quickly to temperature changes, are extremely sensitive to self-heating errors, and have high accuracy, but require the use of a current source, have a smaller temperature measurement range, and are more expensive.
Integrated IC
IC type temperature sensors (temperature integrated circuits) are digital temperature sensors that have a very linear voltage/current-temperature relationship.
Integrated temperature sensors can easily solve most temperature sensing challenges in the -55 to 200ºC temperature range. Because temperature ICs require an external power supply, they are often embedded in circuits and not used for stand-alone probing.
There are many benefits to using IC sensors, including: low power consumption; the availability of small package products (some as small as 0.8mm x 0.8mm); and also low device cost in some applications. In addition, since IC sensors are calibrated during production testing, there is no need for further calibration and they are very easy to use. They are commonly used in fitness tracking applications, wearable products, computing systems, data loggers, and automotive applications.