Ambient Air Quality Sensors: Monitoring the Air We Breathe
Introduction
In an era where environmental concerns are paramount, ensuring the quality of the air we breathe has become increasingly important. Ambient air quality sensors play a crucial role in monitoring and assessing the air around us. These sensors provide real-time data on various pollutants, enabling individuals, communities, and organizations to make informed decisions to protect their health and the environment. This article explores the significance of ambient air quality sensors, their working principles, applications, and the benefits they offer in promoting cleaner and healthier air.
Understanding Ambient Air Quality Sensors
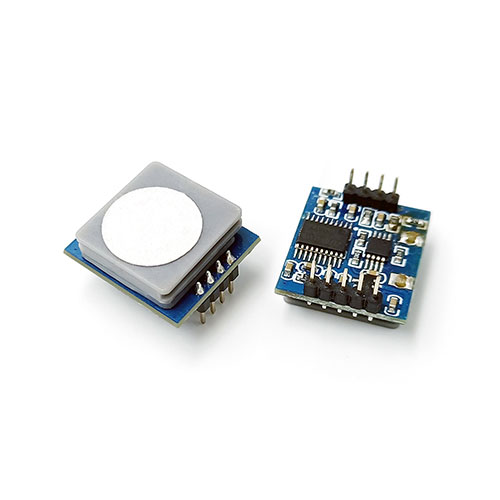
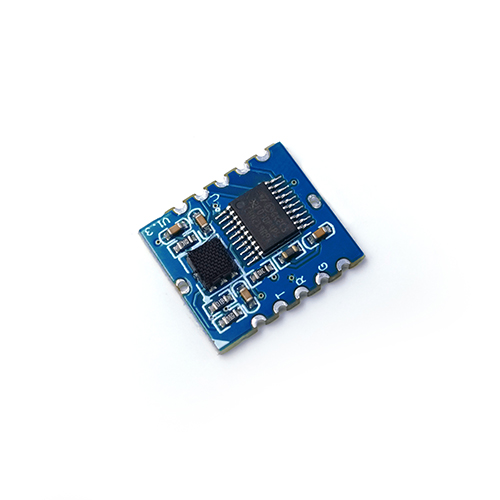
Ambient air quality sensors are electronic devices designed to measure and monitor the presence of pollutants and other harmful substances in the air we breathe. These sensors utilize advanced technologies to detect and analyze various components, including particulate matter (PM), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3).
Working Principles
Ambient air quality sensors employ different techniques to measure air pollutants. Some sensors utilize optical methods, such as light scattering or absorption, to detect particulate matter. Others rely on electrochemical reactions to measure gases like CO, NO2, and O3. Additionally, sensors may use metal-oxide sensors or photoionization detectors to detect VOCs. These sensors work by detecting changes in electrical resistance or measuring the intensity of light absorbed or scattered by the pollutants.
Applications
Ambient air quality sensors find applications in various settings to enable comprehensive air quality monitoring. Here are some key application areas:
Urban Environments:
In cities, ambient air quality sensors are deployed to monitor pollution levels near roads, industrial areas, and densely populated regions. This data helps local authorities develop effective pollution mitigation strategies and inform citizens about air quality levels in their vicinity.
Indoor Spaces:
Indoor air quality sensors are used to monitor pollutants within homes, offices, schools, and other indoor environments. These sensors detect VOCs, CO2, and other harmful substances, allowing individuals to take necessary actions to improve indoor air quality and ensure a healthier living or working environment.
Industrial Facilities:
Ambient air quality monitoring is crucial in industrial facilities to comply with regulations, assess worker safety, and monitor emissions. Sensors are deployed to measure pollutant levels both within the facility and in the surrounding areas.
Environmental Research:
Researchers utilize ambient air quality sensors to collect data on pollution patterns, study the impact of pollutants on ecosystems, and assess the effectiveness of pollution control measures. This research aids in developing sustainable policies and practices to safeguard the environment.
Benefits and Future Potential
The widespread adoption of ambient air quality sensors brings several benefits. By providing real-time data, these sensors empower individuals to make informed decisions about outdoor activities or adjust their indoor environments for better air quality. Communities can use the collected data to advocate for pollution reduction measures and hold accountable the industries causing environmental harm. Moreover, the data collected through these sensors contributes to a better understanding of air pollution patterns, aiding in the development of targeted interventions and policies.
Looking ahead, advancements in sensor technology are likely to make ambient air quality sensors more accurate, portable, and cost-effective. Increased connectivity through the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable a network of sensors, creating comprehensive air quality maps and allowing for better pollution control strategies.
Conclusion
Ambient air quality sensors have become essential tools for monitoring and assessing the air we breathe. By providing real-time data on pollutants, these sensors empower individuals, communities, and organizations to take actions to safeguard their health and the environment. With ongoing advancements in sensor technology and increased awareness about the importance of air quality, these sensors will continue to play a vital role in promoting cleaner and healthier air for all.