Principle and application of infrared CO2 sensor
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an important greenhouse gas, and its concentration is closely related to global climate change. Therefore, monitoring and controlling CO2 concentration is of great significance. Infrared CO2 sensor is a commonly used CO2 concentration detection method. It has the advantages of good selectivity, long life, not dependent on oxygen, little environmental interference, not easy to be poisoned, and high accuracy. It is widely used in smart homes, smart agriculture, industrial gas emissions, and automobile air conditioners. It is widely used in systems and other fields.
Principle of infrared CO2 sensor
Infrared CO2 sensors work based on the non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) principle. The NDIR principle is a principle that uses the different absorption rates of infrared light by different gases to measure gas concentration. CO2 has strong absorption ability under infrared light with a wavelength of 4.26 μm, while other gases have very weak absorption ability at this wavelength of infrared light. Therefore, the infrared CO2 sensor uses an infrared light source to emit infrared light with a wavelength of 4.26 μm. After being absorbed by a gas chamber of a certain length, and then passing through a narrow-band filter with a wavelength of 4.26 μm, the infrared detector monitors the infrared light with a wavelength of 4.26 μm. The intensity of light indicates the concentration of CO2 gas.
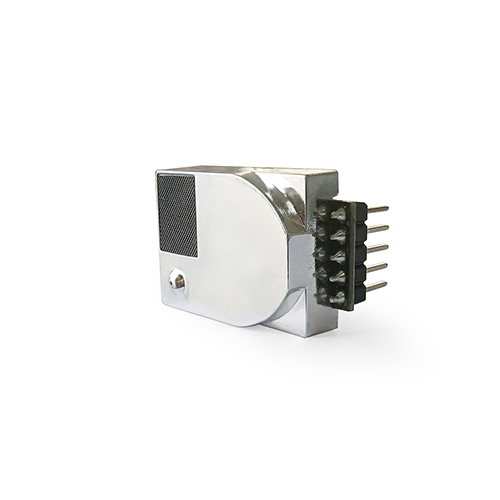
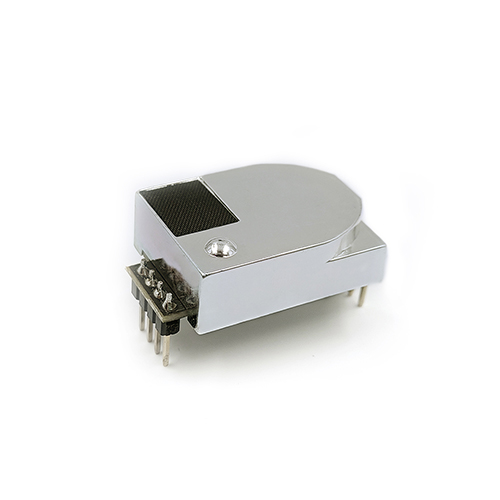
The structure of the infrared CO2 sensor mainly consists of an infrared light source, an air chamber, a narrow-band filter, an infrared detector and a signal processing circuit.
Infrared light source: used to emit infrared light with a wavelength of 4.26μm.
Gas chamber: used to contain the gas to be measured.
Narrowband filter: used to filter infrared light of other wavelengths and only allow infrared light of 4.26μm wavelength to pass through.
Infrared detector: used to detect the intensity of 4.26μm wavelength infrared light that passes through the narrow-band filter.
Signal processing circuit: used to process the signal output by the infrared detector and output the CO2 concentration.
Advantages of Infrared CO2 Sensors
Good selectivity: CO2 has strong absorption ability under infrared light of 4.26μm wavelength, while other gases have very weak absorption ability of infrared light of this wavelength, so the infrared CO2 sensor has good selectivity.
Long life: The infrared CO2 sensor uses a semiconductor detector with a lifespan of more than 10 years.
Not dependent on oxygen: The measurement of the infrared CO2 sensor does not depend on the presence of oxygen, so it can be used to measure the concentration of CO2 in the air.
Less interference from the environment: The infrared CO2 sensor has less interference from environmental factors such as temperature and humidity.
Not easy to be poisoned: The infrared CO2 sensor uses a semiconductor detector, and its working principle is related to the photoelectric effect, so it is not easy to be poisoned.
High accuracy: The measurement accuracy of the infrared CO2 sensor can reach 0.1%~1%.
Applications of infrared CO2 sensors
Smart Home: Infrared CO2 sensors can be used to monitor indoor air quality and automatically adjust the opening and closing of the fresh air system based on CO2 concentration.
Smart agriculture: Infrared CO2 sensors can be used to monitor the CO2 concentration required for plant growth and automatically adjust the ventilation system of the greenhouse based on the CO2 concentration.
Industrial gas emissions: Infrared CO2 sensors can be used to monitor CO2 emissions during industrial production processes and control them based on the emissions.
Car air conditioning system: Infrared CO2 sensors can be used to monitor the CO2 concentration inside the car and automatically adjust the refrigeration and ventilation of the air conditioning system based on the CO2 concentration.