How methane gas detector sensor works
Methane gas detector sensor is a device used to detect the concentration of methane in the air, which has important applications in industrial production, environmental monitoring and safety protection. How does the Methane gas detector sensor work? Next, we will introduce the working principle and application areas of methane sensor in detail.

Methane gas detector sensor working principle
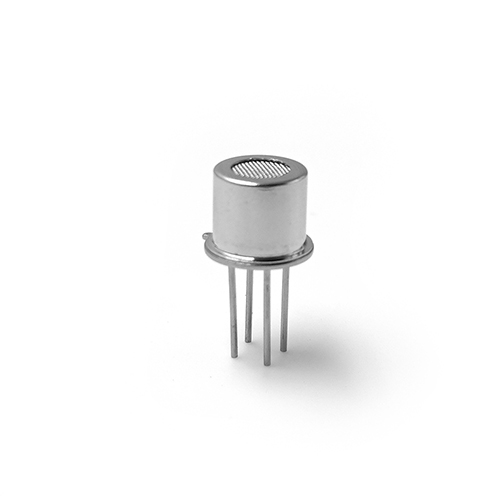
1.The core component of Methane gas detector sensor is the sensing element, which usually adopts semiconductor gas-sensitive element. When the methane concentration in the air changes, the resistance value of the sensing element will change accordingly. The working principle of the sensing element is based on the adsorption and desorption of methane by the gas-sensitive material. When methane molecules are adsorbed on the surface of the gas-sensitive material, the electrical conductivity of the material will be changed, resulting in a change in the resistance value.
2.Methane gas detector sensor also includes signal processing circuit and display parts. The resistance signals collected by the sensing element are amplified, filtered and linearized by the signal processing circuit, and finally converted into voltage or current signals proportional to the methane concentration. These signals are then sent to the display unit for indication, usually in the form of a digital display or an indicator light, of the methane concentration.
3.The operating principle of the methane gas detector sensor also involves temperature compensation and interference suppression. Since the sensitivity of the sensing element is greatly affected by temperature, temperature compensation is required to ensure the accuracy of the sensor at different temperatures. In addition, the sensor needs to suppress interference from other gases to avoid false alarms.
Methane gas detector sensor application areas
Households and public buildings
- kitchens and gas water heaters: detecting the concentration of methane gas produced by kitchen stoves and ovens and water heaters, to prevent the accumulation of gas in the room from reaching the explosive level concentration.
- underground parking lots and subway stations: monitoring methane gas emissions from vehicles to prevent accumulation of excessive methane gas that could lead to safety accidents. 3. shopping malls and theaters: detecting methane gas concentrations in crowded buildings.
- shopping malls and theaters: use methane detectors in densely populated public places to ensure people’s safety.

Industrial and laboratory environments
- Petrochemical companies and chemical laboratories: for monitoring the risk of combustion and explosion of hazardous chemicals and maintaining the safety of workers and experimenters.
- boiler houses and power units: for monitoring methane concentrations in gas and coal combustion to prevent risks such as carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Industries such as steel and mining: for safety testing in environments filled with combustible gases to prevent fires and explosions.

Industries such as mines and oil
- coal mines, gold mines and other mines: used to monitor the concentration of combustible gases in the mine, timely warning to avoid mining accidents.
- crude oil extraction and natural gas production: monitoring methane leakage at the wellhead to ensure the safety of workers and equipment.

Natural gas transmission pipeline
- natural gas transmission stations: used to monitor natural gas stations and pipeline leaks, to prevent methane leaks from gathering to form an explosion hazard.
- City gas pipelines: to protect residents from accidents caused by natural gas leaks.

Environmental monitoring
- wastewater treatment plants: used to detect methane concentration generated in landfills and wastewater treatment processes, to control gas emissions.
- Wetland reserves and greenhouses: to monitor methane release in wetlands and greenhouses to help environmental protection and agricultural management.