How to measure dust particles in air
With the rapid development of urbanization and the continuous advancement of industrialization, air quality has become one of the focuses of people’s attention. Dust particles in the air are an important indicator of air quality, and their measurement is crucial for assessing environmental pollution and protecting human health. This article will introduce some common methods, as well as advanced techniques, for measuring dust particles in the air.
Classification of suspended particulate matter:
Before measuring dust particles in the air, we first need to understand the classification of suspended particles. According to the size of the diameter, suspended particles can be divided into respirable particles (PM10, diameter less than 10 microns), fine particles (PM2.5, diameter less than 2.5 microns) and ultrafine particles (diameter less than 0.1 microns). These different sizes of particles have different effects on human health, so measurements need to take these nuances into account.
Traditional measurement methods:
Particle trap: Traditional particle traps are a common measurement method that captures particles by letting the air pass through filter paper or other adsorbent materials, and then measure the weight to estimate particle concentration. This method is simple and economical, but has certain limitations on the size and composition of particles.
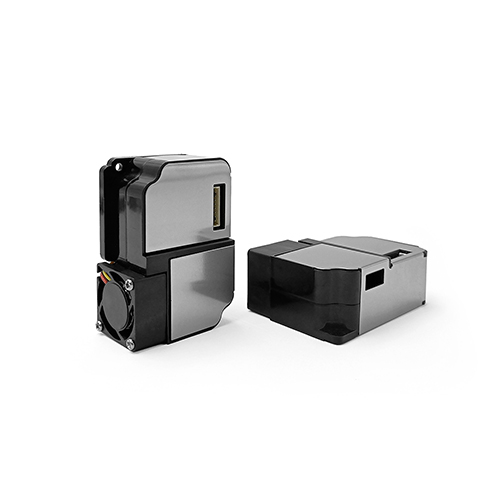
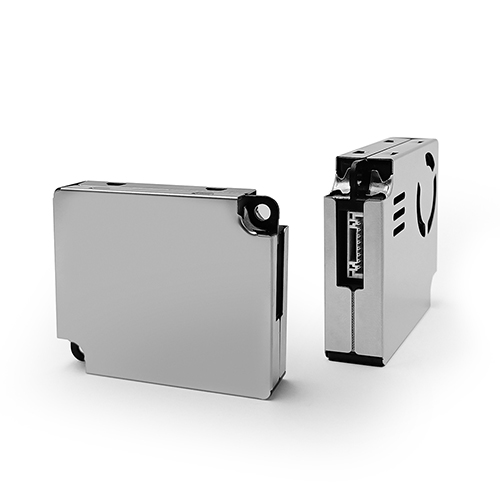
Laser scattering method: Laser scattering method is a measurement method based on optical principles. It uses a laser beam to illuminate particles in the air and calculates the concentration of particles based on the intensity of scattered light. Most of the Particle Matter sensors currently on the market use laser scattering method, which is suitable for detecting indoor air dust particles.
Advanced measurement technology:
LiDAR Scattering: LiDAR Scattering is an advanced measurement technology that uses the high resolution of LiDAR to measure airborne particles. By analyzing the angle and intensity of scattered light, the particle size distribution and concentration information of the particles can be obtained. This method is characterized by high sensitivity and precision, and can deal with particles of different sizes and compositions.
Electron microscopy technology: Electron microscopy technology can directly observe particulate matter at high resolution, and obtain information on the shape, size and composition of particulate matter through image analysis. This method is suitable for detailed characterization and analysis of particulate matter, but the equipment is expensive and the operation is complicated.
Data analysis and application:
Measured dust particle data in the air needs to be effectively analyzed and processed to better understand air quality conditions. Data visualization technology can be used to display measurement results in the form of charts, which can help governments, scientific research institutions and the public better understand environmental conditions and take corresponding measures to improve air quality.
The measurement of dust particles in the air is a critical step in protecting the environment and human health. Traditional particle traps and laser scattering are commonly used measurement methods, while lidar scattering and electron microscopy represent advanced measurement techniques. The comprehensive use of these methods, combined with advanced data analysis technology, can more comprehensively and accurately assess air quality, providing scientific basis for formulating environmental protection policies and improving the urban environment.